NOTE: In case of provisioned disks it is recommended to use eager/thick provisioning instead of thin provisioning
Adding a Disk
On QUADStor startup the system is scanned for all available disks. Available disks do not include disks with mounted partitions. Available disks include software raid disks created using gvinum or mdadm. On linux LVM volumes can also be configured, however once configured the LVM volume should not be resized. Disk partitions can no longer be configured as physical storage.
In order to view the available disks and to configure the storage, Click on the “Physical Storage” menu and select the “View Storage” Submenu
The physical storage detected by the system is listed in the “View Storage” page and is as shown in the figure below
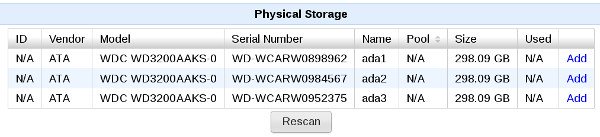
- Click on the “Add” link to add a disk which can be used for virtual disks
In the next page the storage pool for the disk can be selected as shown in the figure below.
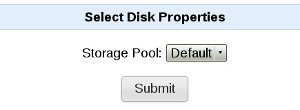
Click on Submit to add the disk. Initialization of the disk will take a few minutes. Wait for the initialization to complete before adding another disk
A disk that was added can be removed later by clicking on the “Remove” link for the disk
In case newer disk storage has been attached to the system, click on the “Rescan” button to rescan for attached storage devices
The first disk added to a pool is considered as the master disk for the pool. This disk can only be removed when all other configured disks and virtual tapes in the pool are removed. The 'Status' column lists the flags assigned to a configured disk. The following are meaning of the flags
- M: The disk is the master disk (first added disk) of the pool
- D: The disk maintains deduplication table metadata
- U: Unmap of unused blocks is enabled for the disk
For e.g a status of 'MU' indicates that the disk is the master disk of the pool and unmap is enabled for the disk.
Command line configuration
List all disks
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -l
Listing all configured disks
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -l -c
Listing all disks excluding configured disks
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -l -e
Add a disk
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -a -d <devicepath> -g <pool name> Where <devicepath> is the value listed under the "Name" column in the output of a bdconfig -l
For example
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -a -d /dev/sda adds /dev/sda to the Default pool
Remove a configured disk
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig -x -d <devicepath>
Unmap unused disk blocks
For disk blocks no longer in use, the VTL can now send UNMAP/TRIM commands to a configured disk
Start scan for unmap blocks
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig --unmapscan 1 -d <devicepath>
Progress can monitored in the VTL system log file and ends with the message "end unmap for bid"
Stop a running scan for unmap blocks
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig --unmapscan 0 -d <devicepath>
Enable unmap when tapes are deleted/erases
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig --unmap 1 -d <devicepath>
When unmap is enabled for a disk a status flag 'U' is displayed for disk in the disk in the "Physical Storage" page. With unmap, when a tape is delete or erased, for the blocks no longer in use UNMAP/Trim commands are sent to the disk.
Enable unmap when tapes are deleted/erases
/quadstorvtl/bin/bdconfig --unmap 0 -d <devicepath>
